ZENER
DIODE:
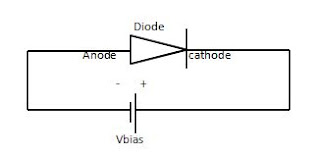
Zener diode is used as a voltage regulator. It provides stable reference at the output and operated always in reversed bias direction. The PN junction is heavily doped to construct the Zener diode, when we diode operated in reversed bias the early breakdown is called Zener breakdown, it’s a normal breakdown all the application is operated in this breakdown after applying higher voltage then the breakdown changed in avalanche breakdown now in this breakdown the diode then not able to use again. The breakdown as
 |
| Zener diode |
In this breakdown the
voltage is greater than the Zener voltage and hence it damaged and flow maximum
voltage. Once time a diode is operated in avalanche breakdown than it can’t use
another time it became useless.
ZENER BREAKDOWN:
Diode can be used again if it operated one time in Zener
breakdown, in this breakdown the voltage is less than the avalanche breakdown
the application is run in Zener test current region. If we considered that the
Zener breakdown is operated in 5V than the avalanche is must greater then
5V.
ZENER IMPENDENCE:
The total resistance
in a circuit is called impendence
From ohm,
V=IR
And
R=V/I
Where
R=Zz, V=Vz, I=Iz
Hence Zener impendence
Zz=∆Vz/∆Iz
NUMERIC 1:
A Zener diode exhibit a certain changed in Vz for a certain
Changed in Iz on a portion of the linear characteristic curve between Izk and
IzM in fig. what is the Zener impendence
Solution:
∆Vz= 50mV
∆Iz= 5mA
Zz=?
Here Zener impendence (Zz)=
Zz= 50mV/5mA
= 10Ω